📘 قراءة كتاب Information Gathering and Diagnosis Development أونلاين


التعويضات السنية Prosthodontics وتشمل
الجسور الثابتة Fixed bridges والزرعات Implants
الطقوم الكاملة المتحركة removable complete denture
الطقوم الجزئية المتحركة removable partial denture
معالجة و إصلاح الأسنان Operative Dentistry وتشمل:
تشخيص تسوس الأسنان caries diagnosis
الوقايه والحد من انتشار تسوس الاسنان management of dental caries
تبييض الأسنان Dentalbleaching
تجميل الأسنان cosmetic dentistry
حشوات الأسنان Dental Fillings
معالجة لب الأسنان Endodontics
معالجة الأسنان المجهرية microscopic endodontics
طب الأسنان الوقائي Preventive Dentistry
تقويم الأسنان Orthodontics
جراحة الفم والوجه والفكين Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
طب أسنان الأطفال Pedodontics
أمراض اللثة
أمراض الأنسجة المحيطة بالأسنان Periodontics
زراعة الأسنان Dental Implantology
أشعة الأسنان Dental Radiology
طب الأسنان الشرعي Forensic Dentistry
طب الفم Oral Medicine
أمراض الفم Oral Pathology
أنسجة الفم والأسنان Oral Histology
المادة السنية Dental material
تشريح الأسنانDental anatomy
مواضيع متعلقة بطب الأسنان
طب الأسنان للرضع
جراحة الأسنان
أسنان
طقم أسنان
طب الاسنان في الاردن
طب الأسنان في جميع أنحاء العالم
Information Gathering and Diagnosis Development
Dental Diagnoses
Pulpal and Periapical Diagnoses
Documentation
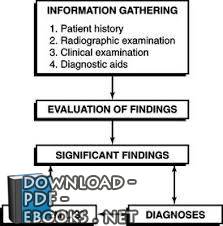
Accurate diagnostic information forms the foundation
of any treatment plan. This information comes from
several sources: the patient history, radiographs, and the
clinical examination. The dentist must critically analyze
the information before recommending treatment options
to the patient. The goal of this chapter is to discuss both
the types of data that the dentist in general practice typically
collects and the ways in which the dentist evaluates
and documents this information in preparation for
creating a treatment plan.
OVERVIEW OF THE
DIAGNOSTIC PROCESS
The diagnostic process is begun by gathering information
about the patient and creating a patient database
from which all future decisions will be made. Although
the components of each patient’s database vary, each
includes pieces of information, or findings, that come
from asking questions, reviewing information on forms,
observing and examining structures, performing diagnostic
tests, and consulting with physicians and other
dentists.
Findings fall into several categories. Signs are findings
discovered by the dentist during an examination. For
instance, the practitioner may observe that a patient has
swollen ankles and difficulty in breathing when reclined,
signs suggestive of congestive heart failure. Findings
revealed by the patients themselves, usually because they
are causing problems, are referred to as symptoms.
Patients may report such common symptoms as pain,
CHAPTER OUTLINE
Overview of the Diagnostic Process
Information Gathering
Patient History
Techniques for Obtaining a Patient History
Questionnaires and Forms
Patient Interviews
Components of a Patient History
Demographic Data
Chief Complaint and History
General Health History
Oral Health History
Psychosocial History
Clinical Examination
Physical Examination
Intraoral and Extraoral Examination
Periodontal Examination
Examination of the Teeth
Occlusion
Radiographic Examination
Other Diagnostic Aids
Study Casts
Diagnostic Wax-Ups and Altered Casts
Occlusal Splints
Caries Excavation
Consultations
Medical Laboratory Tests
Biopsy
Microbiologic and Other Testing Systems
Developing Diagnoses and Problem Lists for
Patients
Benefits of Creating Diagnosis and Problem
Lists
Common Diagnoses
General Health Diagnoses
Psychosocial Diagnoses
Intraoral/Extraoral Diagnoses
Periodontal Diagnoses
4 The Treatment Planning Process
كتب طب اسنان
كتب طبية باللغة العربية pdf
كتب طب اسنان مترجمة
كتب تقويم اسنان بالعربي
كتب طب الاسنان في مصر
كتب طب اسنان بالعربي pdf
البسيط في تقويم الأسنان pdf
كتب طب اسنان سنة اولى
تحميل كتب في تقويم الاسنان
حجم الكتاب عند التحميل : 9.7 ميجا بايت .
نوع الكتاب : pdf.
عداد القراءة:
اذا اعجبك الكتاب فضلاً اضغط على أعجبني و يمكنك تحميله من هنا:

شكرًا لمساهمتكم
شكراً لمساهمتكم معنا في الإرتقاء بمستوى المكتبة ، يمكنكم االتبليغ عن اخطاء او سوء اختيار للكتب وتصنيفها ومحتواها ، أو كتاب يُمنع نشره ، او محمي بحقوق طبع ونشر ، فضلاً قم بالتبليغ عن الكتاب المُخالف:
 قبل تحميل الكتاب ..
قبل تحميل الكتاب ..
يجب ان يتوفر لديكم برنامج تشغيل وقراءة ملفات pdf
يمكن تحميلة من هنا 'http://get.adobe.com/reader/'

 منصّة المكتبة
منصّة المكتبة